What is a WAN Computer Network
When you think about connecting multiple locations, a WAN (Wide Area Network) comes to mind. It's more than just a network; it's the backbone for businesses that operate across vast distances. By linking local networks, it enables seamless communication and resource sharing. But as you explore the intricacies of WANs, you'll discover both their advantages and the challenges they present, shaping how organizations function today. What else lies beneath the surface?
Definition of a WAN
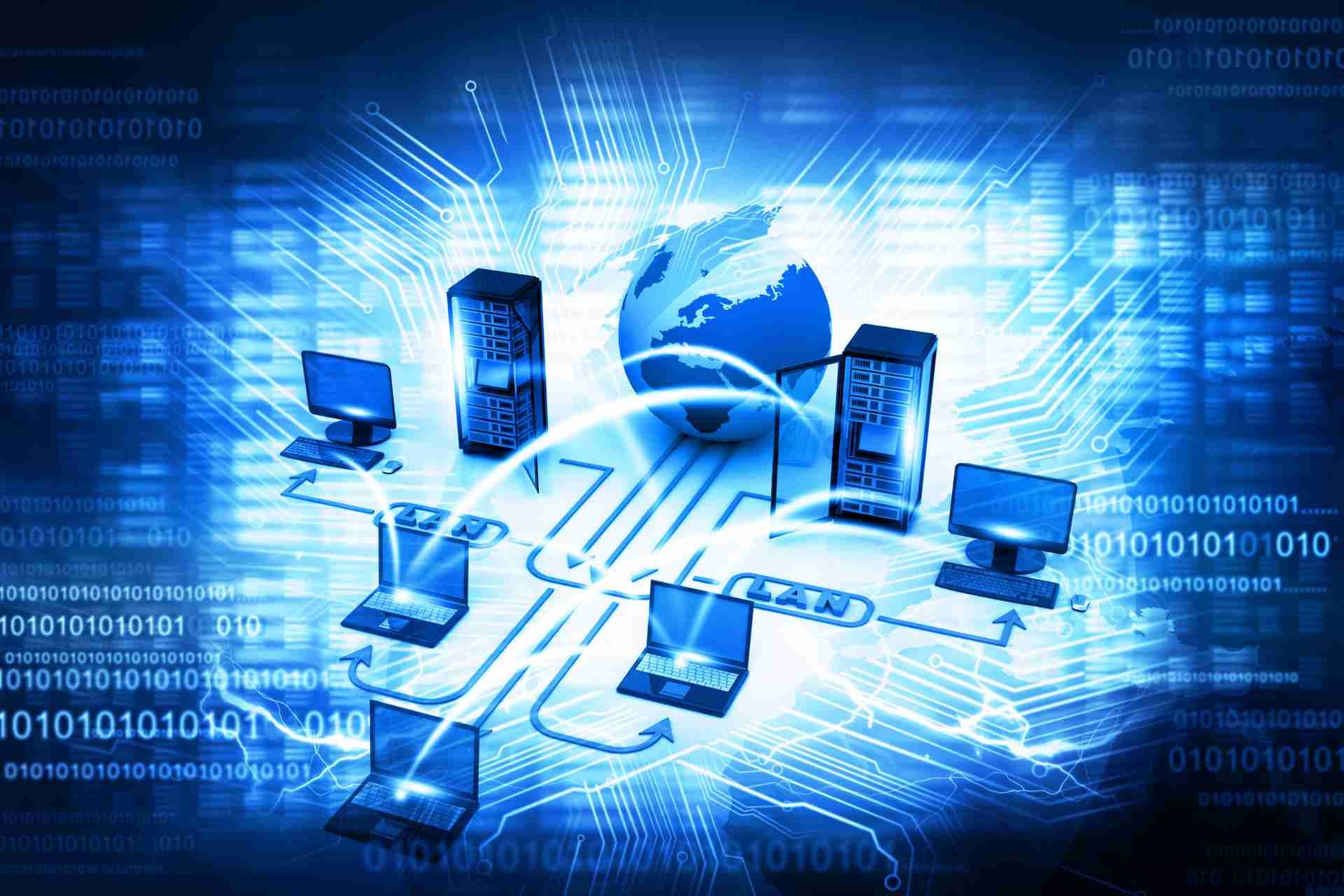
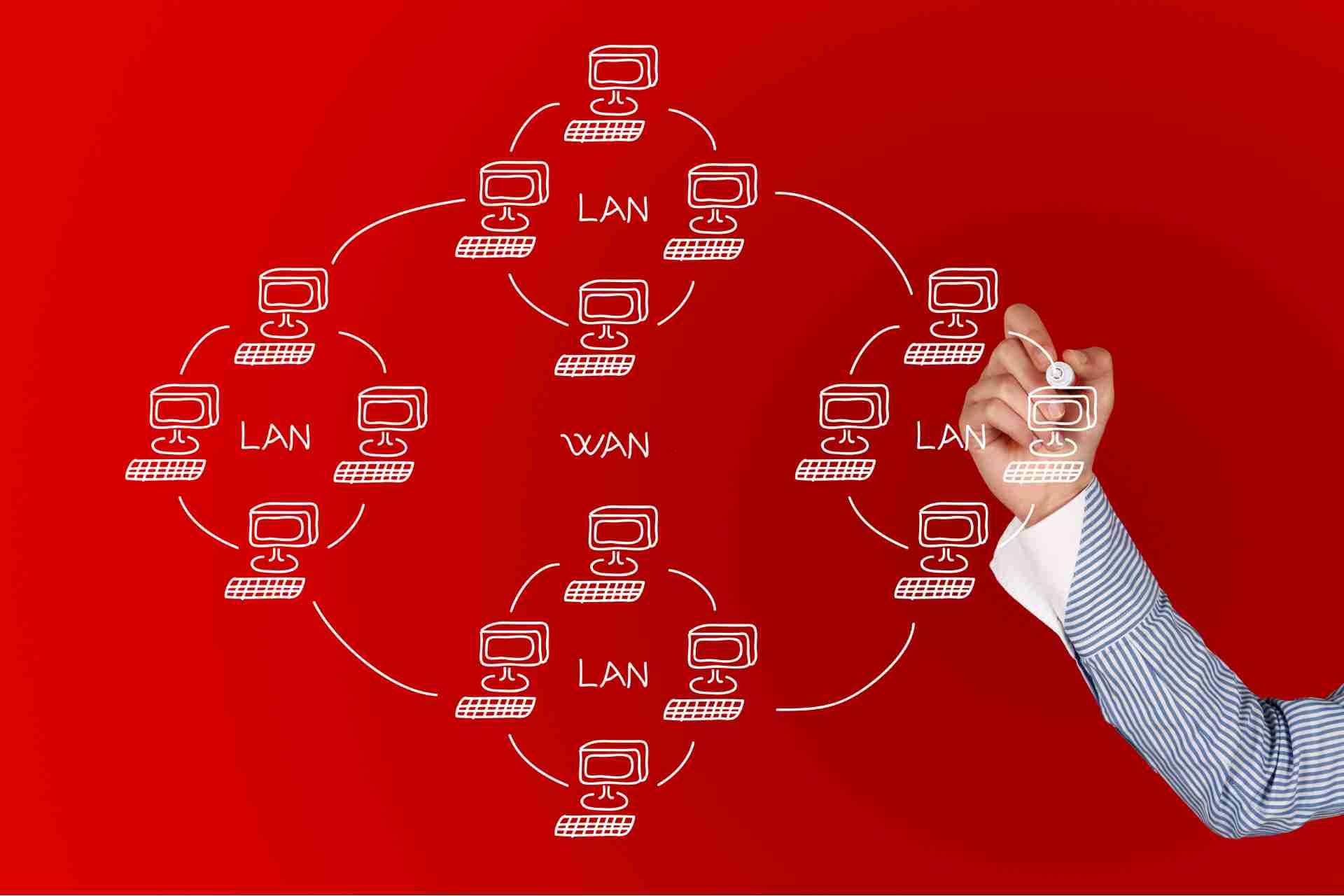
A Wide Area Network (WAN) connects multiple local area networks (LANs) across large geographical distances, allowing users to communicate and share resources seamlessly.
You'll find that WANs typically span cities, countries, or even continents, making them essential for businesses with multiple locations.
Unlike a LAN, which serves a limited area, a WAN enables broader connectivity, supporting various communication technologies such as leased lines, satellite links, and fiber optics.
This versatility means you can access data remotely, utilize cloud services, and collaborate with teams worldwide.
WANs also play a critical role in connecting different devices and networks, ensuring that information flows efficiently across vast distances.
Understanding this definition is fundamental to grasping how networks function on a global scale.
Key Characteristics of WANs
WANs boast several key characteristics that set them apart from other network types. First, they cover large geographic areas, connecting users over cities, countries, or even continents. This extensive reach allows you to communicate and share data across vast distances.
Additionally, WANs often rely on various communication technologies, including leased lines, satellites, and public networks, providing flexibility in connectivity options. They also support a high number of users and devices, making them ideal for large organizations.
Security is another essential characteristic, with encryption and secure protocols ensuring safe data transmission.
Finally, WANs typically require more complex management and maintenance due to their size and diversity, making skilled IT personnel crucial for optimal performance.
Types of WAN Technologies
Several types of WAN technologies cater to different connectivity needs and requirements.
You might encounter leased lines, which provide dedicated, reliable connections between locations.
Another option is MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), known for its efficiency and ability to manage traffic effectively.
If you're looking for cost-effective solutions, consider VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), which utilize existing internet infrastructure to secure data transmission.
Satellite connections are also available, especially in remote areas where traditional connections may not reach.
Finally, 4G and 5G cellular networks offer wireless WAN options, providing flexibility and high-speed connectivity on the go.
Each of these technologies has its advantages, so think about your specific needs when deciding which one best fits your organization.
How WANs Operate
Understanding the various WAN technologies lays the groundwork for grasping how these networks operate. WANs connect multiple local area networks (LANs) across large distances, enabling communication between users in different locations. They use various transmission methods, such as leased lines, satellite links, and fiber optics, to send and receive data efficiently.
When you send data over a WAN, it travels through routers and switches that direct the traffic to its destination. Protocols, like MPLS and ATM, help manage data flow and ensure reliable delivery.
Advantages of Using a WAN
While you might consider various networking options for your business, the advantages of using a WAN are hard to overlook. A WAN connects multiple locations, allowing you to share resources and data seamlessly across vast distances. This means your team can collaborate effectively, regardless of where they're situated.
You'll also enjoy centralized data management, enhancing security and reducing redundancy. With a WAN, you can scale your network easily as your business grows, accommodating new branches or remote workers without major disruptions.
Plus, you'll likely reduce costs over time by consolidating services and utilizing cloud solutions. Ultimately, a WAN provides the flexibility and efficiency that helps your business thrive in today's interconnected world.
Challenges and Limitations of WANs
Despite their many advantages, WANs come with challenges and limitations that businesses must navigate. One major issue is latency, which can slow down data transmission and affect performance, especially for real-time applications.
Additionally, WANs often rely on third-party providers, making you vulnerable to outages or service disruptions. Security is another concern; transmitting data over large distances increases the risk of interception and cyberattacks.
Bandwidth limitations can also hinder performance, especially during peak usage times. Furthermore, the complexity of managing a WAN can strain IT resources, requiring specialized knowledge and ongoing maintenance.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for maximizing the benefits of your WAN and ensuring seamless connectivity across your organization.
WAN vs. LAN vs. MAN
When comparing network types, it's essential to recognize the distinct roles of WANs, LANs, and MANs.
A WAN, or Wide Area Network, connects multiple locations over long distances, like cities or countries. You'll often see it used by businesses with remote offices.
On the other hand, a LAN, or Local Area Network, operates within a limited area, such as a home or office, allowing devices to communicate quickly and efficiently.
Meanwhile, a MAN, or Metropolitan Area Network, serves a larger area than a LAN but is smaller than a WAN, typically covering a city or a large campus.
Understanding these differences helps you choose the right network type based on your specific connectivity needs.
Applications of WANs in Business
As businesses expand across regions and countries, they increasingly rely on Wide Area Networks (WANs) to facilitate seamless communication and collaboration. WANs enable you to connect multiple offices, share resources, and access centralized data, no matter where you are.
This connectivity supports real-time communication tools like video conferencing and instant messaging, enhancing teamwork across distances. Additionally, WANs allow for the integration of cloud services, making it easier for employees to access applications and data from anywhere.
They also support secure data transfer, protecting sensitive information as it travels between locations. By leveraging WANs, you can streamline operations, improve productivity, and maintain a competitive edge in today's global market.
Future Trends in WAN Technology
The reliance on WANs in business has set the stage for exciting advancements in WAN technology.
You'll see increased adoption of Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN), which offers enhanced flexibility and cost savings. This technology lets you manage your network more efficiently, adapting traffic flows based on real-time needs.
Additionally, more companies will embrace cloud-based WAN solutions, improving scalability and connectivity across global locations.
Artificial intelligence (AI) will play a significant role in optimizing performance and security, allowing your systems to self-heal and respond to potential threats automatically.
Lastly, the integration of 5G technology will provide faster and more reliable connections, empowering your team to work seamlessly from anywhere.
Stay ahead by embracing these trends in your WAN strategy.
Setting Up and Managing a WAN
Setting up and managing a WAN involves careful planning and execution to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
First, assess your organization's needs and determine the necessary bandwidth and redundancy. Choose the right WAN technology, whether MPLS, VPN, or SD-WAN, based on your specific requirements.
Next, establish connections between sites, ensuring proper routing and addressing. Implement security measures like firewalls and encryption to protect data.
Regularly monitor network performance using tools that provide real-time analytics. This helps you identify bottlenecks and address issues promptly.
Train your staff on best practices for WAN management, including troubleshooting and maintenance.
Finally, stay updated on technology advancements to keep your WAN efficient and secure over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a WAN is essential for connecting multiple locations, supporting efficient communication and resource sharing across vast distances. By understanding its characteristics, technologies, and advantages, you can leverage a WAN to enhance your business operations. While challenges exist, the benefits of centralized data management and scalability far outweigh them. As WAN technology continues to evolve, staying informed will help you adapt and optimize your network for future needs. Embrace the power of a WAN to drive your organization forward.