Small Business Office Network Setup

Small businesses today rely heavily on technology to operate efficiently and effectively. One key component of this technology is the office network.
Setting up an office network is a crucial step for ensuring seamless communication, efficient data management, and overall productivity in a business environment. Whether you are establishing a network for a small office or a larger corporate setting, following a systematic approach is essential to creating a reliable, secure, and scalable network. This guide will walk you through the key steps and considerations for setting up an office network.
Assess Your Needs
Start by evaluating the specific needs of your office network. Consider factors such as:
- The number of employees and devices that will connect to the network
- Types of applications and services required (e.g., file sharing, email, VoIP, cloud services)
- The need for remote access and VPN (Virtual Private Network)
- Data storage and backup requirements
- Future scalability to accommodate business growth
Design the Network Layout
Design a network layout that optimizes performance and coverage. This includes:
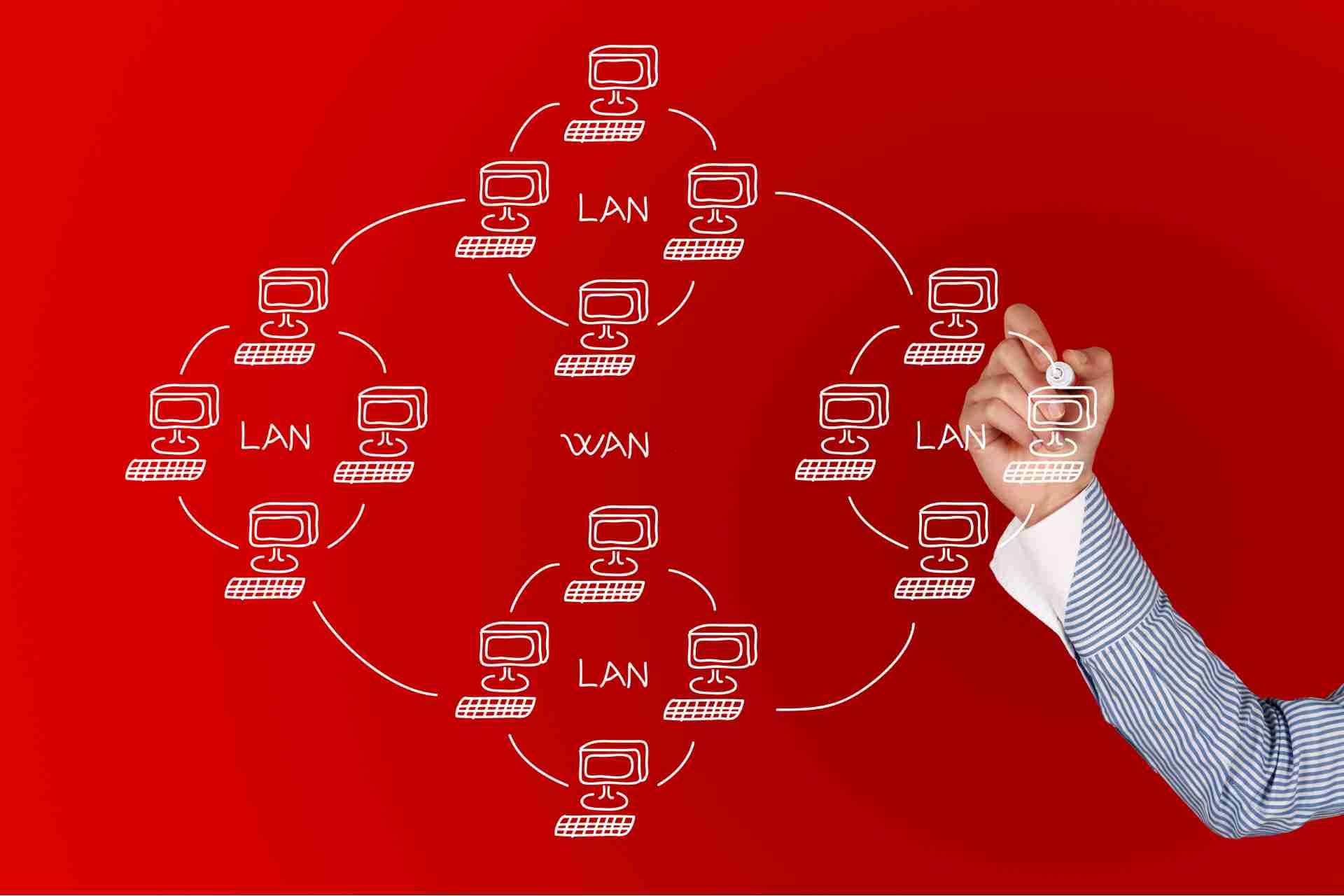
Topology
Decide on the network topology (star, bus, ring, or hybrid) that best suits your office layout and requirements. The star topology, where each device is connected to a central switch, is commonly used for its reliability and ease of management.
Wired vs. Wireless
Wired connections, often referred to as Ethernet connections, involve running cables from each device to a central networking hub. This setup provides a stable and consistent connection with fast speeds, making it ideal for tasks that require heavy bandwidth, such as large file transfers or video conferencing. Wired connections are also generally more secure, as they are harder to intercept compared to wireless signals.
On the other hand, wireless connections offer more flexibility and convenience. They allow users to connect to the network from anywhere within the office without the need for cables, making it easier to move around and collaborate with colleagues. Wireless networks are also easier to set up and maintain, as there is no need to run cables through walls or ceilings. However, wireless connections can be prone to interference from other devices or nearby networks, which can lead to slower speeds or dropped connections.
Choose Network Hardware
Select the appropriate hardware to build your network:
- Router: Acts as the gateway between your office network and the internet. Choose a router with sufficient speed, security features, and support for the number of devices on your network.
- Switches: Connect multiple devices within the network. Managed switches offer advanced features like VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) and QoS (Quality of Service) for better control and performance.
- Access Points: Provide wireless connectivity. Ensure they support the latest Wi-Fi standards (e.g., Wi-Fi 6) for optimal performance.
- Cabling: Use high-quality Ethernet cables (Cat6 or higher) for wired connections to ensure reliable and fast data transfer.
- Firewall: Protects your network from unauthorized access and cyber threats. A dedicated hardware firewall provides robust security features.
Configure IP Addressing
Set up a logical IP addressing scheme for your network:
- Static vs. Dynamic IPs: Use static IP addresses for critical devices (e.g., servers, printers) and dynamic IP addresses (assigned by DHCP) for other devices.
- Subnetting: Divide your network into subnets to improve performance and security. For example, separate subnets for different departments or types of devices.
Implement Network Security
Security is paramount in any office network setup. Key measures include:
Firewall Configuration
Configuring a firewall is a crucial step in ensuring your network's security. By properly configuring your firewall, you can restrict access to sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access to your network, and block malicious traffic from entering your system. Here are some important tips for configuring a firewall:
1. Determine your security requirements: Before you start configuring your firewall, it's important to understand your security needs. Consider the type of data you are trying to protect, the potential threats your network faces, and the level of access you want to grant to users. This will help you determine which security rules to implement in your firewall.
2. Choose the right firewall solution: There are different types of firewalls available, including hardware firewalls, software firewalls, and cloud-based firewalls. Choose the one that best suits your network's needs and capabilities.
3. Create security rules: Once you have chosen a firewall solution, you will need to create security rules to determine how traffic is allowed or blocked. For example, you can create rules to block certain IP addresses, ports, or protocols, or allow access only to specific users or devices.
4. Regularly update and monitor your firewall: Security threats are constantly evolving, so it's important to keep your firewall up to date with the latest security patches and updates. Additionally, monitor your firewall logs regularly to identify any suspicious activity and adjust your security rules accordingly.
5. Test your firewall configuration: Once you have configured your firewall, it's important to test it to ensure that it is working as intended. Test for vulnerabilities, check for any misconfigurations, and make any necessary adjustments to improve your network's security.
VPN
One way to ensure secure remote access to the office network is by establishing a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection between an employee's device and the office network, preventing hackers and cybercriminals from intercepting sensitive information.
Setting up a VPN is relatively simple and can be done by following a few easy steps. First, you will need to purchase a VPN service from a reputable provider. There are many options available, so be sure to choose one that offers strong encryption and other security features.
Next, install the VPN software on your device and configure it to connect to the office network. This may require inputting settings provided by your IT department. Once the VPN is set up, you can securely access the office network from anywhere in the world..
Wireless Security
Use strong encryption (e.g., WPA3) for Wi-Fi networks and implement SSID hiding and MAC address filtering.
User Authentication
User authentication is crucial for protecting sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access to accounts. Without proper authentication measures in place, malicious actors can easily gain access to personal and confidential data, leading to identity theft, financial loss, and reputation damage.
Regular Updates
Keep firmware and software up-to-date to protect against vulnerabilities.
Set Up Network Services
Configure essential network services:
- File Sharing: Set up file servers or NAS (Network Attached Storage) devices for centralized file storage and sharing.
- Email Server: Configure an email server or use cloud-based email services.
- VoIP: Implement a VoIP system for internet-based phone services.
- Backup Solutions: Establish regular data backup routines to prevent data loss.
Test and Troubleshoot
Before rolling out the network to all users, conduct thorough testing:
Connectivity
Testing the connectivity of an office network is an important task that should be regularly performed to ensure that everything is running smoothly. There are several reasons why testing connectivity is crucial:
1. Identify potential issues: By testing the connectivity of the office network, IT professionals can identify any potential issues or bottlenecks that may be impacting the performance of the network. This allows them to quickly address and resolve any problems before they escalate and cause disruptions to the business operations.
2. Ensure optimal performance: Regularly testing the connectivity of the office network helps to ensure that it is performing at its best. IT professionals can monitor factors such as bandwidth usage, latency, and packet loss to identify any areas that may need improvement in order to optimize the network's performance.
3. Prevent downtime: Downtime can be costly for businesses, as it can result in lost productivity and revenue. By testing the connectivity of the office network on a regular basis, IT professionals can proactively identify any potential issues that may lead to downtime and take the necessary steps to prevent it from occurring.
So, how can you test the connectivity of your office network? There are several tools and methods that can be used to assess the performance of the network:
1. Ping tests: Ping tests are a simple way to check the connectivity between devices on a network. By sending a small packet of data to a specific IP address and measuring the time it takes for a response to be received, IT professionals can determine the latency and packet loss of the network.
2. Bandwidth testing: Bandwidth testing tools can be used to measure the speed and capacity of the network connection. By running bandwidth tests at different times of the day, IT professionals can identify any fluctuations in performance and address any issues that may be impacting the network's speed.
3. Network monitoring software: Network monitoring software allows IT professionals to continuously monitor the performance of the office network in real-time. By setting up alerts for certain network metrics, such as bandwidth usage or latency, IT professionals can quickly identify any issues and take action to resolve them before they impact the business.
Performance
Test network speed and performance under typical usage conditions.
- Bandwidth: This is the amount of data that can be transmitted over the network at a given time. A high bandwidth allows for faster data transfer speeds and better performance. You can test your office network's bandwidth using a speed test tool, which will measure the upload and download speeds of your connection.
- Latency: Latency is the delay between sending data and receiving a response. High latency can cause lag and slow performance. You can test your office network's latency using a ping test, which measures the time it takes for a data packet to travel from one point to another on the network.
- Packet loss: Packet loss occurs when data packets are lost during transmission. This can lead to errors and performance issues. You can test for packet loss using a packet loss test, which will measure the percentage of packets lost during data transmission.
Security
Perform security assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Conducting security assessments helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses within your network. By conducting regular assessments, you can proactively address any security gaps before they are exploited by cybercriminals. This not only helps protect sensitive data and information, but also prevents costly data breaches that can harm your business’s reputation and bottom line.
There are several key areas to focus on when performing a security assessment of your office network. These include:
1. Network infrastructure: Assess the security of your network infrastructure, including routers, switches, firewalls, and other devices. Ensure that all devices are up to date with the latest security patches and configurations are properly set up to prevent unauthorized access.
2. User access controls: Review user access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data and systems. Implement multi-factor authentication and strong password policies to enhance security.
3. Data encryption: Encrypting sensitive data is crucial to protecting it from unauthorized access. Ensure that data is encrypted both at rest and in transit to prevent data leaks and breaches.
4. Security policies and procedures: Review and update security policies and procedures to ensure compliance with industry regulations and best practices. Regularly train employees on cybersecurity awareness and protocols to prevent human error-related security breaches.
5. Incident response plan: Develop an incident response plan that outlines steps to be taken in the event of a security breach. Conduct regular drills and simulations to test the effectiveness of the plan and make necessary adjustments.
Documentation and Training
Document your network setup and provide training to employees:
- Network Documentation: Maintain records of IP addresses, device configurations, network topology, and security settings.
- User Training: Educate employees on best practices for network use, security policies, and troubleshooting basic issues.
Ongoing Maintenance and Monitoring
Regularly maintain and monitor your network to ensure optimal performance and security:
- Monitoring Tools: Use network monitoring tools to track performance, detect issues, and generate alerts.
- Updates and Patches: Regularly update firmware, software, and security patches.
- Audits: Conduct periodic network audits to identify and mitigate potential risks.